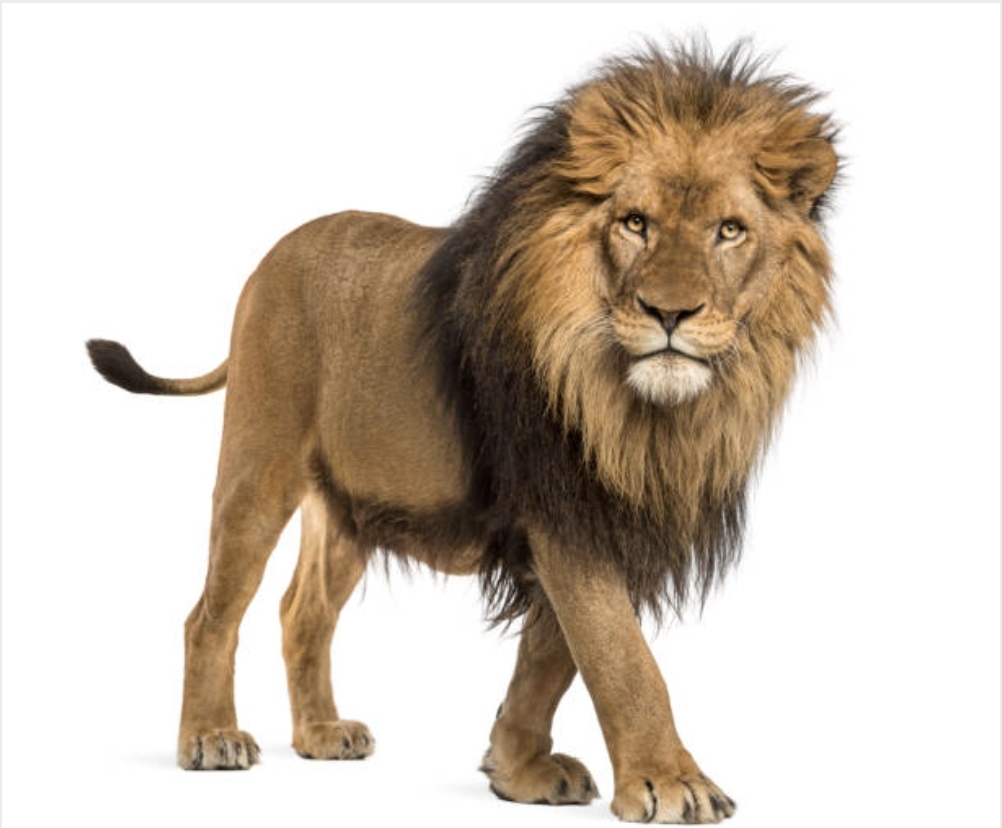
In the vast, open savannas of Africa, the lion Panthera leo stands as an emblem of strength, courage, and nobility. Revered in cultures worldwide and symbolized in everything from ancient myths to modern corporate logos, lions embody a unique blend of power and grace. This documentary explores the life of lions, their roles within their ecosystems, and the profound lessons humans can learn from these magnificent creatures.
The Social Fabric of Lion Prides
Lions are the only truly social big cats, living in structured groups known as prides. These prides typically consist of related lionesses, their offspring, and a small number of adult males, usually brothers or close kin.
Leadership and Hierarchy
– Male Lions Coalitions: A pride’s male lions, often a coalition of brothers, are responsible for defending the pride’s territory against rival males and predators. Their presence and strength ensure the safety of the pride, and they work together to repel intruders.
– Female Lions (Lionesses): The lionesses are the pride’s hunters and caretakers. They coordinate hunting strategies and share the responsibility of raising the cubs. Their roles highlight the power of collective leadership and the importance of nurturing and protection within a community.
Community and Cooperation
– Hunting and Sharing:Lionesses hunt in groups, often using complex strategies to ambush prey. This cooperative hunting allows them to take down larger and faster animals than they could manage alone. After a successful hunt, food is shared among the pride, ensuring that even the youngest and weakest members are nourished.
– Raising the Young:All lionesses in the pride contribute to raising and protecting the cubs, a communal effort that increases the survival chances of the offspring. This shared responsibility underscores the importance of collective effort and the social bond within the pride.
The Role of Lions in the Ecosystem
Lions are apex predators, playing a critical role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. Their presence helps regulate the populations of herbivores and influences the health of their environment.
Balancing Prey Populations
– Natural Regulation: By preying on large herbivores like zebras, wildebeests, and buffaloes, lions help keep these populations in check. This prevents overgrazing, which can lead to habitat degradation and a decline in biodiversity.
– Promoting Biodiversity: The presence of lions supports a diverse range of species. By controlling herbivore numbers, they allow vegetation to flourish, which in turn supports other wildlife, from insects to birds and smaller mammals.
Scavengers’ Lifeline
– Resource Sharing:The carcasses left by lions provide essential food for a variety of scavengers, including hyenas, vultures, and smaller carnivores. This shared food source helps sustain other species, contributing to the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
– Nutrient Cycling: The remains of lion kills contribute to nutrient cycling in their habitats, enriching the soil and promoting plant growth, which supports the entire food web.
Lessons from Lion Society
Lions, through their behavior and social structure, offer several valuable lessons for human societies.
Strength in Unity
– Collective Strength: The combined force of a lion pride illustrates the power of unity and teamwork. Just as lions rely on each other for hunting and protection, humans can achieve greater accomplishments through collaboration and mutual support.
– Cooperation and Coordination: The intricate coordination among lionesses during a hunt demonstrates the importance of working together towards a common goal. This principle is applicable in various human endeavors, from business to community projects.
2. Resilience and Adaptability
– Adapting to Change: Lions are remarkably adaptable, capable of thriving in diverse environments from the African savannas to the fringes of deserts. Their ability to adjust to different habitats and overcome challenges teaches us the importance of flexibility and resilience in facing life’s uncertainties.
– Survival Against Odds:*Lions often face threats from rival prides, human encroachment, and changing environmental conditions. Their perseverance in the face of adversity resonates with the human spirit, encouraging us to remain resilient and adaptive.
Leadership and Responsibility
– Protective Leadership:The role of male lions in defending their pride showcases qualities such as bravery, responsibility, and sacrifice. Similarly, lionesses’ dedication to hunting and caring for the young reflects strength and commitment.
– Guiding and Nurturing: Effective leadership in human societies requires guiding and protecting communities, much like the roles within a lion pride. Leaders can learn from lions the importance of balancing strength with nurturing to support and uplift their communities.
The Lion’s Decline: A Call to Action
Despite their critical role and iconic status, lions face significant threats that have led to a dramatic decline in their population. Habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and poaching are among the primary challenges endangering these majestic animals.
Habitat Preservation
– Protecting Natural Habitats: Ensuring lions have access to their natural habitats is essential for their survival. Conservation efforts focus on preserving savannas, forests, and grasslands where lions thrive, and establishing protected areas and wildlife corridors to connect fragmented habitats.
– Sustainable Development: Balancing human development with the need to protect natural habitats is crucial. Sustainable land-use practices can help mitigate habitat loss and provide lions with the space they need to live and hunt.
Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation
– Reducing Conflicts: As human populations expand into lion territories, conflicts arise, often leading to the killing of lions. Innovative solutions, such as improved livestock management, the use of deterrents, and compensation schemes for farmers, can reduce these conflicts and promote coexistence.
– Community Engagement:Educating and engaging local communities about the importance of lions and the benefits of conservation can foster a sense of stewardship and support for protecting these iconic animals. Community-based conservation programs that involve local people in decision-making and benefit-sharing are essential for sustainable lion conservation.
Combatting Poaching and Illegal Trade
– Anti-Poaching Measures: Strengthening anti-poaching efforts and law enforcement is crucial to protect lions from illegal hunting and trade. This includes equipping rangers, improving surveillance, and enhancing legal frameworks to deter poachers.
– Demand Reduction: Reducing demand for lion products, such as bones and skins, through awareness campaigns and stricter regulations, is vital to curb illegal trade and protect lion populations.
Lions, with their majestic presence and complex social structures, offer a unique window into the natural world. They embody lessons in unity, resilience, and leadership that resonate deeply with human values. As we strive to protect these magnificent creatures, we honor not only their role in our ecosystems but also the profound wisdom they impart.
Lions remind us of the beauty and complexity of life on Earth and our responsibility to safeguard it. By conserving lions, we preserve a legacy of strength, courage, and community that can inspire and guide us for generations to come.
Sources:
1. National Geographic. “Lions 101.” [National Geographic](https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/lion).
2. World Wildlife Fund. “Lion.” [WWF](https://www.worldwildlife.org/species/lion).
3. Panthera. “Lion.” [Panthera](https://www.panthera.org/cat/lion).
4. BBC Earth. “The Real Lives of Lions.” [BBC](https://www.bbcearth.com/blog/?article=the-real-lives-of-lions).
5. African Wildlife Foundation. “Lions.” [AWF](https://www.awf.org/wildlife-conservation/lion).
6. International Union for Conservation of Nature. “Panthera leo.” [IUCN Red List](https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/15951/123651288).
Through understanding and appreciating the life of lions, we gain insights into the intricate balance of nature and our place within it. Lions, as both symbols and teachers, remind us of the enduring strength and unity that can inspire and shape our journey.